某些时候我们写的程序会意外崩溃。有些时候的崩溃是必然出现的,有些时候是随机的出现的。随机出现的崩溃问题,一般查找崩溃的原因需要花费很多时间,不过如果要是有崩溃的 log ,就能很快的定位到问题的所在了。相信大家有些对 SQA 打的一些随机一次、有规律重现的 bug 都很头痛吧。现在介绍一个办法能抓住崩溃的现场 log 日志,这样就能快速的定位崩溃的原因。
原理
这个办法就是:捕获全局异常。java 程序的大多数崩溃都是异常引起的(注意这里说的是一般,这个方法其实是有限制的,具体的后面会说到)。如果发生了异常,你捕获了,那么系统会把让你的程序来处理异常,如果你没有捕获,那么系统最后会自己处理:那就是挂掉你的程序,然后打印一些崩溃信息。我们现在要做的处理这些没有被程序捕获(处理)的异常(这些异常会引起崩溃),这就是捕获全局异常的原理。但是要注意的一点是:这里捕获全局异常的作用,仅仅是抓取异常(崩溃)的现场日志,方便查找问题而已,不能防止程序崩溃。也就是说就算你捕获了全局异常,也无法阻止你出错的程序挂掉。
实现
我们就来看看如何来实现这个功能吧。首先是新建一个异常处理类 CrashHandler 实现 UncaughtExceptionHandler,这个接口有一个 uncaughtException 方法。当发生了崩溃异常的时候,就会调用这个方法让你来处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
| public class CrashHandler implements UncaughtExceptionHandler { ... ... @Override public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable ex) { if (!handleException(ex) && null != mDefaultHandler) { mDefaultHandler.uncaughtException(thread, ex); } } .... .... private boolean handleException(Throwable ex) { if (ex == null) { return true; } ex.printStackTrace(); if (!needCatchCrash()) { selfKill(); return true; } collectCrashDeviceInfo(); saveCrashInfoToFile(ex); if (needUpload()) { sendCrashReportToServer(getLastCrashReportFile()); } if (needReport()) { autoRestart(); } else { selfKill(); } return true; } ... ... }
|
可以看到 handleException 处理流程是:
- 调用 ex.printStackTrace 打印当前的异常信息。
- 收集运行崩溃程序的设备信息。
- 将崩溃的时候堆栈信息(log)保存到文件。
- 显示崩溃报告界面。
这里有一个可以添加的功能:那就是如果以后有服务器支持,可以向服务器发送崩溃日志信息(类似于一些手机平台sdk,像友盟这种),这样在正式发布产品的时候如果出了错误,也能第一时间发现(当然最好是不出问题)。
收集运行崩溃程序的设备信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
| private void collectCrashDeviceInfo() { try { PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager(); PackageInfo pi = pm.getPackageInfo(mContext.getPackageName(), PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES); if (pi != null) { mDeviceCrashInfo.put(VERSION_NAME, pi.versionName == null ? "unknow" : pi.versionName); mDeviceCrashInfo.put(VERSION_CODE, String.valueOf(pi.versionCode)); mVersionName = (pi.versionName == null ? "unknow" : pi.versionName); mVersionCode = pi.versionCode; } } catch (NameNotFoundException e) { if (DEBUG) LogUtils.e(TAG, "Error while collect package info", e); } Field[] fields = Build.class.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { try { field.setAccessible(true); String key = field.getName(); Object value = field.get(null); mDeviceCrashInfo.put(key, value != null ? value.toString() : value); if (PRODUCT.equals(key)) { mProduct = (value != null ? value.toString() : "unknow"); } } catch (Exception e) { if (DEBUG) LogUtils.e(TAG, "Error while collect crash info", e); } } }
|
这里首先会收集崩溃程序的版本号(VersionCode),然后会收集崩溃程序运行的系统的一些信息(系统的一些编译信息),然后保存在一个 Properties 对象(mDeviceCrashInfo)中。
接下来是保存崩溃时候的堆栈信息了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56
| private void saveCrashInfoToFile(Throwable ex) { Writer info = new StringWriter(); PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(info); ex.printStackTrace(printWriter); Throwable cause = ex.getCause(); while (null != cause) { cause.printStackTrace(printWriter); cause = cause.getCause(); } String result = formatStackTrace(info.toString()); printWriter.close(); mDeviceCrashInfo.put(STACK_TRACE, result); try { String logPath = resolveLogPath(); if (null == logPath) { LogUtils.e(TAG, "log path invalid, can't save crash log file !!"); return; } String fileName = resolveLogFileName(); if (null == fileName) { LogUtils.e(TAG, "log file name invalid, can't save crash log file !!"); return; } String filePath = logPath + File.separator + fileName; if (!StoreUtils.checkFileDirExisted(filePath)) { LogUtils.e(TAG, "save crash info: create crash file dir error !"); return; } checkCacheSize(); FileOutputStream trace = new FileOutputStream(filePath); mDeviceCrashInfo.store(trace, ""); trace.flush(); trace.close(); if (DEBUG) LogUtils.e(TAG, "save a crash file: " + logPath + fileName); } catch (Exception e) { if (DEBUG) LogUtils.e(TAG, "an error occured while writing report file...", e); } }
|
可以看得到,抓取崩溃的堆栈信息是通过将 java 系统抛出的异常 Throwable 打印到我们之前的那个变量 mDeviceCrashInfo 中,然后再把这个变量里面的信息(全都是 String)保存到指定文件来实现的。这里的保存路径(resolveLogPath),我是做了个接口,可以让程序自由设置的。然后这里还限制了一下崩溃文件的大小,如果保存的崩溃文件数量大小超过一定限制,就会去清理一下。具体的代码我这里就不贴了,大家可以自己去看看。
然后最后显示下崩溃报告界面:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35
| private void autoRestart() { Intent intent; intent = new Intent(mContext, CrashReportActivity.class); intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_ANIMATION); PendingIntent contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(mContext, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); AlarmManager mgr = (AlarmManager) mContext .getSystemService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE); recordReStartCount(); if (isReStartTooMany()) { mgr.cancel(contentIntent); selfKill(); return; } mgr.set(AlarmManager.RTC, System.currentTimeMillis() + 300, contentIntent); if (DEBUG) LogUtils.d(TAG, "we restart the app"); selfKill(); }
|
这里的崩溃报告界面(CrashReportActivity)是程序中的一个专门用来显示刚刚保存的崩溃信息的 activity 。这里显示这个 activity 的原理是,设一个短时间的闹钟,然后自己杀死已经发生崩溃了的进程,闹钟到时间后,启动显示崩溃信息的 activity 。这里注意,必须杀是原来已经崩溃了的进程,然后重新启动,才能正常启动程序中的 activity,因为原来的进程已经发生了崩溃异常了,程序已经不正常了,不杀死重启的话,是无法再启动 activity 的。这也是前面的说的为什么这个方法无法阻止程序挂掉的原因。
这个 activity 会调用 CrashHandler 的 loadLastCrashReport 接口来读取最后一次保存的崩溃信息来显示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
| public String loadLastCrashReport() { StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(sw); Properties properties = new Properties(); String crFile = getLastCrashReportFile(); if (null != crFile) { File cr = new File(crFile); try { FileInputStream is; is = new FileInputStream(cr); properties.load(is); pw.println(crFile + " -----"); printProperties(properties, pw); properties.clear(); pw.println(); pw.println(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return sw.toString(); }
|
activity 的代码我就不贴了,具体的大家也可以去看代码。
最后弄一个设置处理未获取异常的接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
| public void init(Context context) { String defLogPath = DEFAULT_CRASH_LOG_PATH + context.getPackageName() + File.separator; init(context, CRASH_HANDLE_FLAG_CATCH, defLogPath, DEFAULT_CRASH_CACHE_SIZE); } public void init(Context context, int flag, String logPath, long crashCacheSize) { mContext = context; mPkgName = context.getPackageName(); mHandleFlag = flag; mLogPath = logPath; mCrashCacheSize = crashCacheSize; mCountFilePath = context.getCacheDir().toString() + File.separator + "CrashLaunchCount.sav"; } public void registerCrashHandler() { mDefaultHandler = Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(); Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(this); }
|
使用方法
自定义一个 Application ,然后在 onCreate 的时候设置一下捕获全局异常的处理就行了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
| public class CustomApplication extends Application implements ActivityLifecycleCallbacks { ... ... @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); init(); } private void init() { CrashHandler.getInstance().init(this); setCrashLogPath(); CrashHandler.getInstance().setCrashCacheSize(CRASH_CACHE_SIZE); CrashHandler.getInstance().registerCrashHandler(); ... ... } ... ... }
|
这里调用 CrashHandler 提供的设置捕获全局异常的接口(init),然后设置了一下保存崩溃文件的路径和崩溃文件的大小限制。如果在某些情况下不想要这个功能,你可以弄个开关,注释掉这3句话就行了,使用起来还是很简单的。因为要写文件,最后别忘记在 manifest 中加上写文件权限和把 application 设置为自己自定义的就行了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
| <application android:name=".lib.CustomApplication" android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > ... ... </application>
|
限制
这个方法也不是万能,也存在一些限制:
- 它只能捕获崩溃挂掉的情况。也就是说,如果不是挂掉的问题,而是一些逻辑 bug 或是界面刷新不对的,这个方法是没用的。
- 它只能捕获有异常发生的情况。如果是 JNI 里面导致一些内存访问越界而导致程序崩溃,这个方法也是没用的。
- 它不能用来拯救程序的,原因之前说过了,这个方法的功能简单来话说:仅仅是抓 log 。
最后上个效果图(demo里面一个故意的空指针访问):
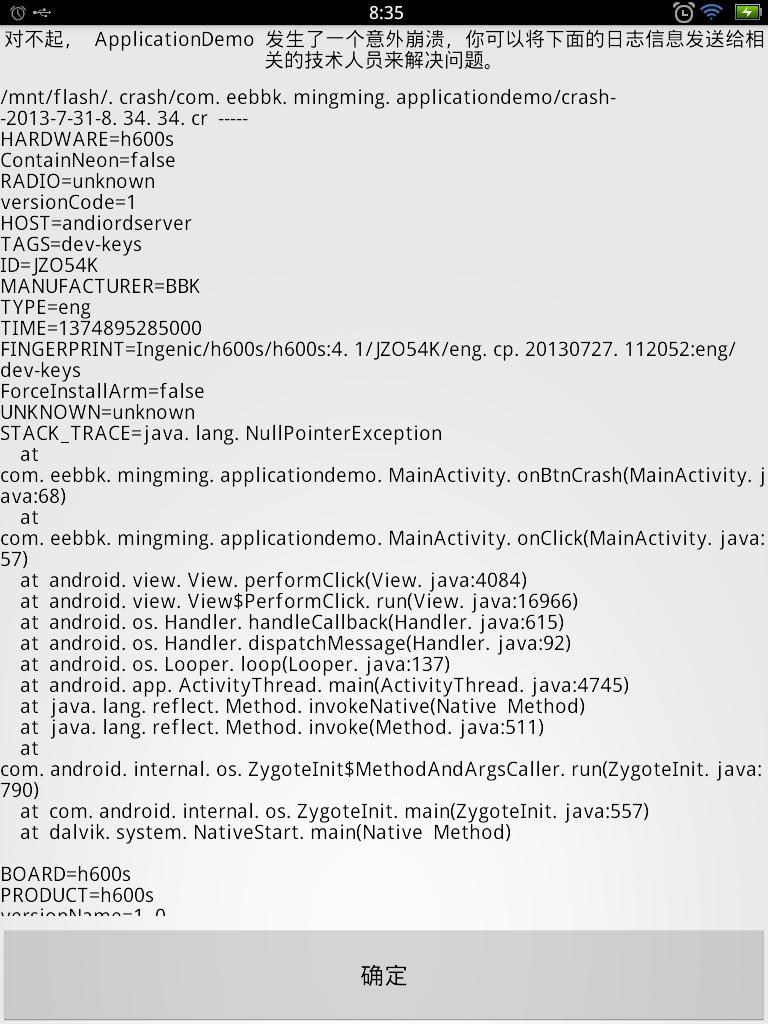
附上参考代码(后续改进了下,project 直接编不过的,需要稍微改一下): ApplicationDemo.tar.gz
